In today’s regulatory landscape, anti-money laundering (AML) audit is emerging as a key element of compliance. AMLYZE, a leading company in this field, underlines the importance of complying with the latest AML guidelines, which encourage companies to consider setting up an independent audit function.
AML audits are essential in assessing and improving a company’s internal control systems, policies and procedures to ensure that they comply with AML regulations. They not only assess the procedures in place, but also evaluate how employees adhere to these procedures in practice through sample testing.
AMLYZE emphasizes the value of an independent audit function that provides an objective and unbiased assessment of a company’s AML/CFT compliance programme, thereby helping to identify and mitigate potential risks. It is also worth mentioning that the AML audit can be carried out internally or outsourced to a third party, especially in cases where the institution does not have the appropriate competence to carry out the AML audit, as it requires specific knowledge and understanding of the latest regulatory requirements.
The rationale behind stringent AML audit requirements
Ensuring the effectiveness of an AML audit programme is more than data collection. It involves establishing and continually updating and monitoring a robust audit programme. The process involves several key steps:
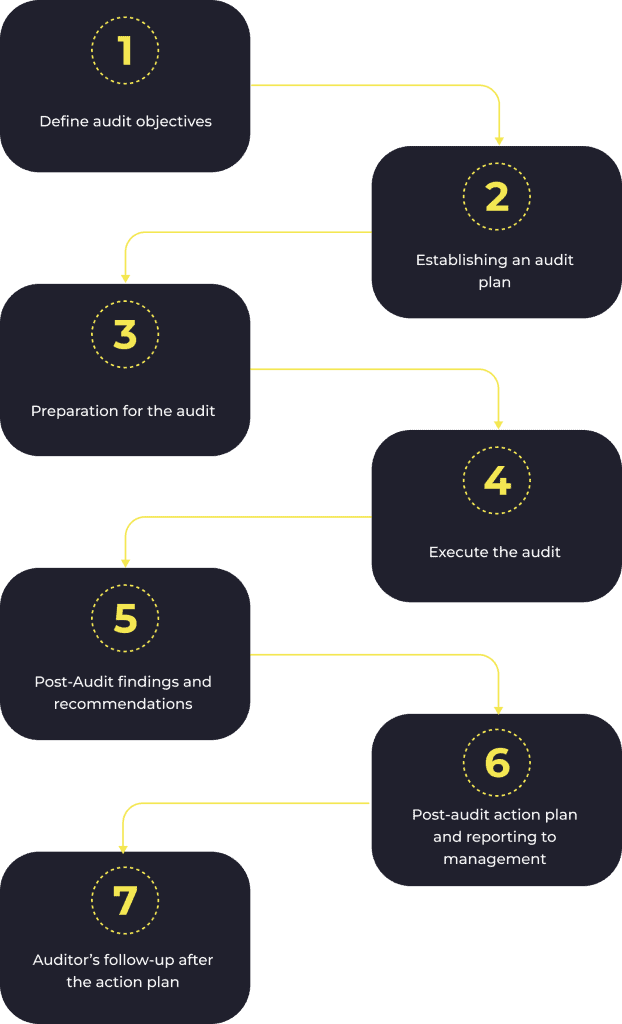
- Define audit objectives: Audits should have clear objectives, whether they are routine or for specific purposes. Selecting auditors with in-depth knowledge of AML laws and regulations is critical, as inexperienced auditors may overlook critical liabilities.
- Establishing an audit plan: Establishing an audit plan is critical to achieving the audit objectives efficiently. The audit plan should be much more detailed than the audit objectives and should include a description of the areas to be audited and the audit methodology. When preparing the audit plan, it may also be beneficial to review previously conducted AML audits.
- Preparation for the audit: Usually, an AML audit is a very extensive and comprehensive process that requires a lot of information, documents and data to be gathered, so in order for the process to run smoothly, it is useful not only for the auditors to prepare in advance, but also to help the department being audited to prepare, for example by explaining the process, schedules and deadlines, possible documentation that will be required, etc.
- Execute the audit: The audit should be executed in accordance with the audit plan to assess the AML compliance programme. In addition, if during the audit the auditors identify significant deficiencies in other AML areas not included in the original plan, consideration should be given to expanding the scope of the audit.
- Post-Audit findings and recommendations: After completion of the audit, it is important not only to describe what was found, but also to evaluate the findings based on their negative impact on the AML compliance programme and to make recommendations to improve the quality and effectiveness of the company’s AML compliance.
- Post-audit action plan and reporting to management: Once the audit is complete, its findings and recommendations should be presented to senior management and an action plan drawn up to address any deficiencies and implement recommendations.
- Auditor’s follow-up after the action plan: It is good practice for the auditor to follow up on actions completed by the auditee to check that recommendations have been properly implemented. It is also good practice to follow up not only on updated or newly adopted procedures but also on a small sample of client cases to assess whether deficiencies have been addressed not only on paper but also in practice.
The scope of an independent AML audit
An independent AML audit is an in-depth review of a company’s AML compliance programme.
This is distinct from a financial audit and may include a review of the firm’s AML programme and policies, enterprise-wide risk assessment, individual customer risk scoring, customer identification procedures, customer due diligence (CDD), enhanced customer due diligence (CDD), ongoing CDD and EDD, review of transaction monitoring systems and procedures, sanctions screening systems, periodic testing and back-testing of these systems, evaluation of other software used for AML purposes, procedures for internal investigations and submission of Suspicious activity reports (SARs), implementation of internal controls and quality assurance processes, AML training, record keeping, three lines of defense framework, reporting to senior management, management of conflicts of interest.
Previous audit reports are also reviewed to assess the effectiveness of the implementation of previous recommendations.
Responsibility and frequency
An AML audit can be carried out internally by staff not involved in money laundering risk areas, i.e. a separate independent line of defense, or by a third party.
Recognising the limitations of smaller companies in terms of resources and expertise, it is often recommended that competent, independent third parties be used for this purpose. However, even if the audit is carried out by an independent third party, the financial institution itself is responsible for the quality of the audit and must therefore carefully select external auditors with sufficient competence.
Requirements vary from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, but there is general agreement that audits should be conducted on a regular basis. For example, in the United States, the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN) has stated that the scope and frequency of testing should be commensurate with the risks posed by the company’s products and services.
The depth and frequency of audits should be commensurate with the risks posed by the firm’s products and services. It is also common practice, particularly in larger financial institutions, for different AML areas to be audited each year, but the scope and depth of the audit will be much greater than if all AML areas were audited in the same year.
AML and financial audits
Unlike a financial audit, which is conducted by a certified public accounting firm and involves a review of financial statements, an AML audit focuses on verifying the adequacy and effectiveness of a company’s anti-money laundering programme.
A comprehensive and informative database is essential to any audit, whether it’s a financial audit or an AML audit. A robust database provides easily retrievable information at multiple levels, providing valuable insight into the complexity of the processes and transactions being audited.
It also enables auditors to gain deeper insights into context, underlying risks and potential anomalies. Maintaining a high quality database is therefore critical to ensuring thorough and reliable audit procedures, ultimately enhancing the effectiveness and trustworthiness of audit findings and recommendations.
AMLYZE emphasizes the importance of maintaining a robust database for client risk assessment and transaction monitoring processes. This ensures easy retrieval of valuable information essential for AML audits.
Conclusions
AML audits are a critical component in ensuring compliance with AML regulations. AMLYZE promotes the need for independent, thorough and effective audits and recognises their role in protecting against financial crime. By rigorously adhering to these audit standards, organizations not only comply with regulatory requirements, but also strengthen their reputation and operational integrity in the face of evolving financial risks.
FAQs:
1. What is an AML audit?
An anti-money laundering (AML) audit is a thorough review of a company’s AML policies, procedures and compliance practices. It assesses the effectiveness of a company’s measures to prevent and detect money laundering activities.
2. Who needs an AML audit?
Any business subject to AML regulations, such as financial institutions, law firms and other entities involved in financial transactions, requires an AML audit to ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations.
3. How often should an AML audit be conducted?
The frequency varies depending on the size of the organization, the nature of the business and regulatory requirements. Typically, financial institutions and businesses with a higher risk profile should conduct it annually.
4. Who can perform an AML audit?
This can be conducted by internal staff not directly involved in the AML compliance process, or by independent third party auditors with expertise in AML regulations and practices.
5. What does an AML audit include?
It includes a review of the AML compliance programme, policies and procedures (from customer risk identification, customer due diligence, transaction monitoring and suspicious activity reporting to the internal control framework).
6. Why is an AML audit important?
They are critical to identifying AML weaknesses, ensuring regulatory compliance, protecting against financial crime and maintaining the integrity of financial systems.
7. What are the consequences of failing an AML audit?
Failure can lead to regulatory sanctions, fines, reputational damage, the omission of transactions related to money laundering or terrorist financing due to weak AML controls and, in severe cases, criminal charges against the company or its officers.
8. How can a business prepare for an AML audit?
Companies can prepare by ensuring their AML policies are up to date, conducting internal reviews, training staff and maintaining proper records of all AML-related activities.
9. What is the difference between an AML audit and a financial audit?
While a financial audit focuses on the accuracy and integrity of financial statements, an AML audit specifically examines the effectiveness of a company’s measures to prevent and detect money laundering activities.